The biosynthesis of glutathione (GSH) involves two sequential reactions that utilize ATP and that are catalyzed by the enzymes glutamate-cysteine ligase and glutathione synthetase using the three precursor amino acids L-glutamic acid, L-cysteine, and glycine.
RiboCeine (D-Ribose L-Cysteine) supplies the body with the needed components to stimulate this biosynthesis of glutathione in mammalian cells.
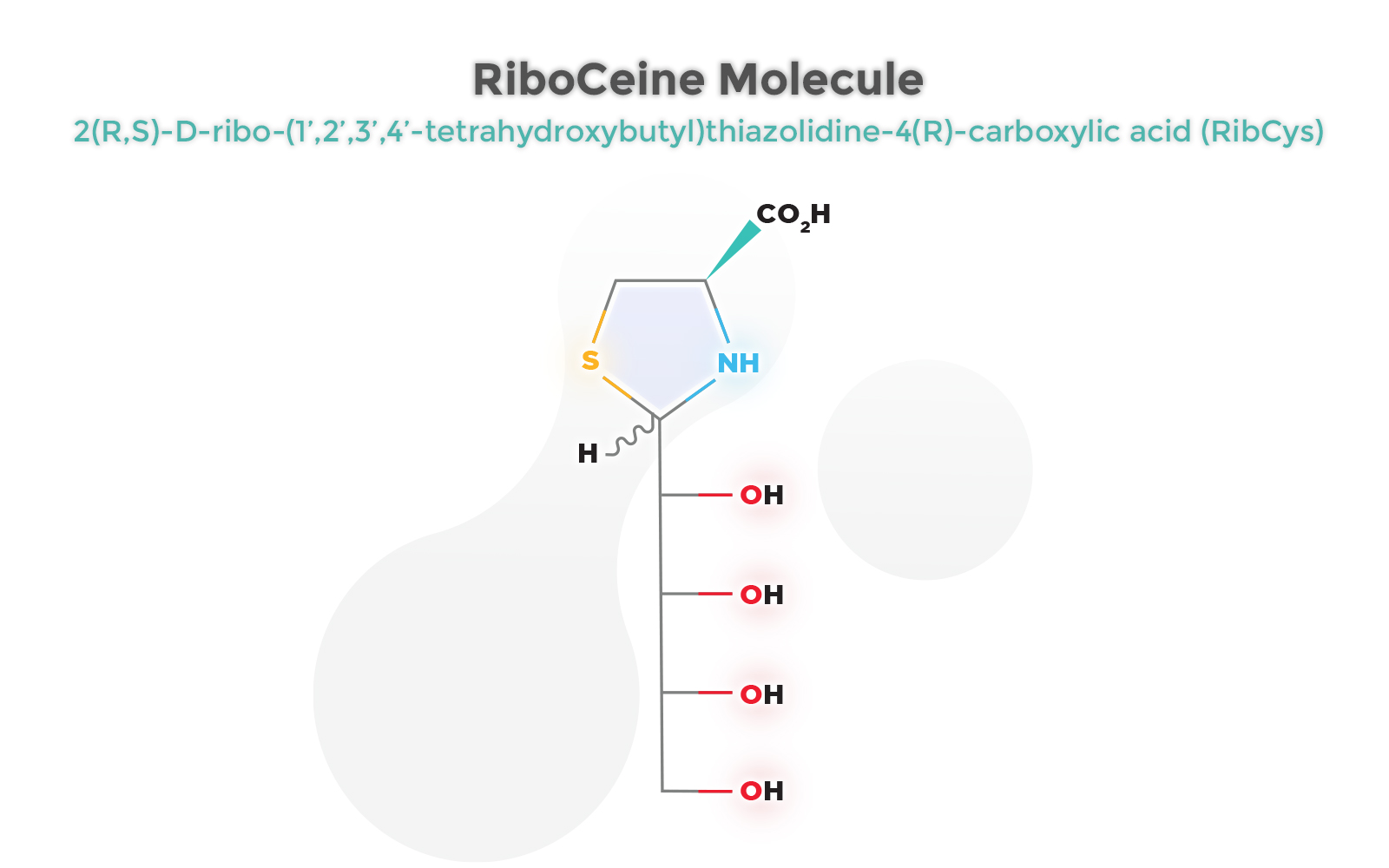
Because Cysteine itself can be neurotoxic when administered to mammals in high doses and degrades when ingested, RiboCeine delivers a bioavailable form of L-cysteine by releasing the sulfhydryl amino acid in vivo by non-enzymatic ring opening via hydrolysis. The liberated L-cysteine then stimulates hepatic glutathione biosynthesis.
In addition to functioning as a prodrug for Cysteine, the administration of RiboCeine delivers D-Ribose to support adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis.
For full details on this unique MOA, please review U.S. Patent #8,501,700.
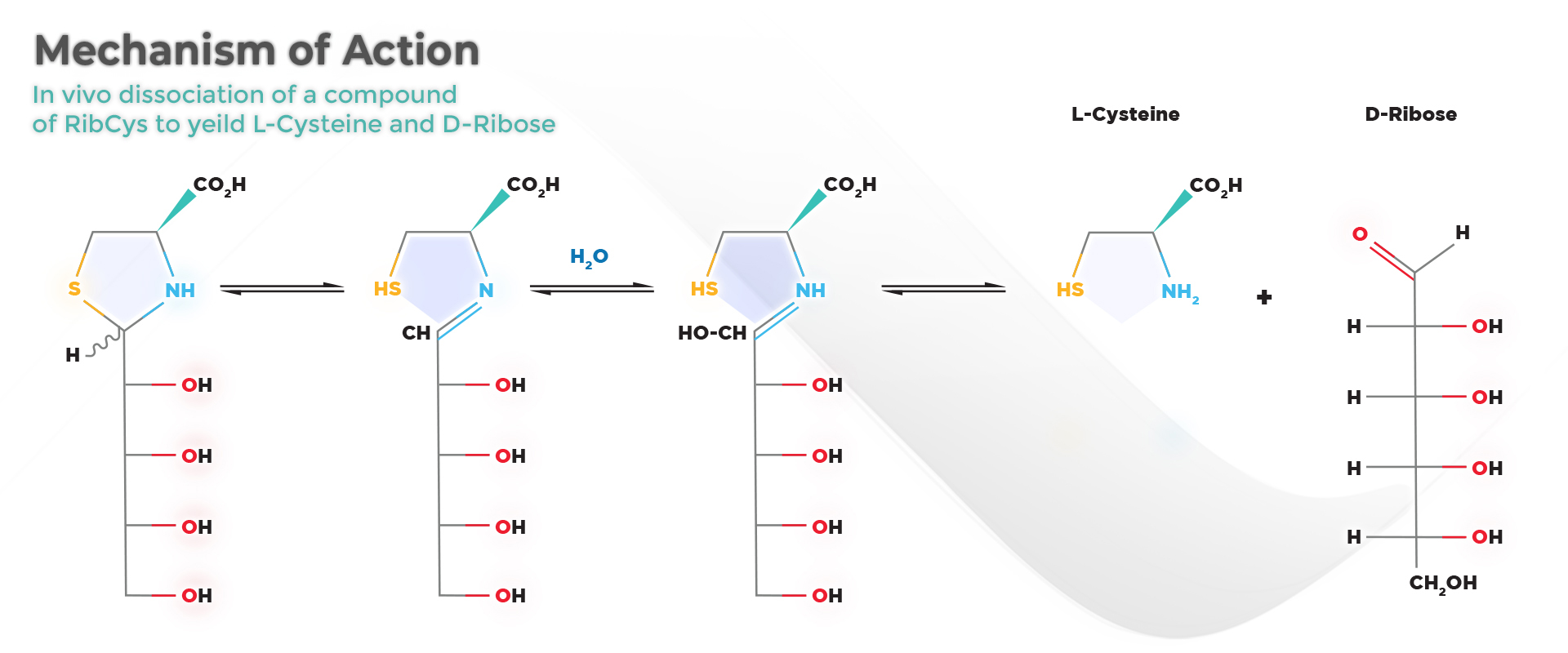
Following in vivo administration, RibCys releases cysteine by non-enzymatic hydrolysis. As well as functioning as a prodrug for cysteine, RibCys can deliver amounts of ribose to ATP-depleted tissues that stimulate the in vivo synthesis of ATP.